It’s a fast-growing world and incremental changes are the one which are constant, everyone learns from their mistakes and experiments they did in past. In software development, it started with Waterfall, then the era of Agile came, and now we are discussing about DevOps and Its extended branch which is CI/CD, stands for Continuous integration/Continuous Delivery. It is now a days a hot rising approach of complete automation of software development life cycle. DevOps have changed the trend of application deliveries, which can be in the shortest span of weekly, daily or even couple of times in a day.
Software development teams have absorbed the fast delivery cycles by incorporating automation in the software delivery pipeline, majorly using Jenkins and the individual loosely coupled development is named as Microservice. CI or Continuous Integration is the part of pipeline where each microservice is part of the delivery integrated to the previous build. Such Integrations occur at each microservice delivery. These integrations help in detection of bugs introduced while integrating the microservices at very early stage, sometime even multiple times in a day. The output which you get is much more filtered.
And now through continuous delivery one can see the building of the product and can analyze and suggest the needful changes to be done. The implantation of CI/CD pipeline involves automating each step of software development.
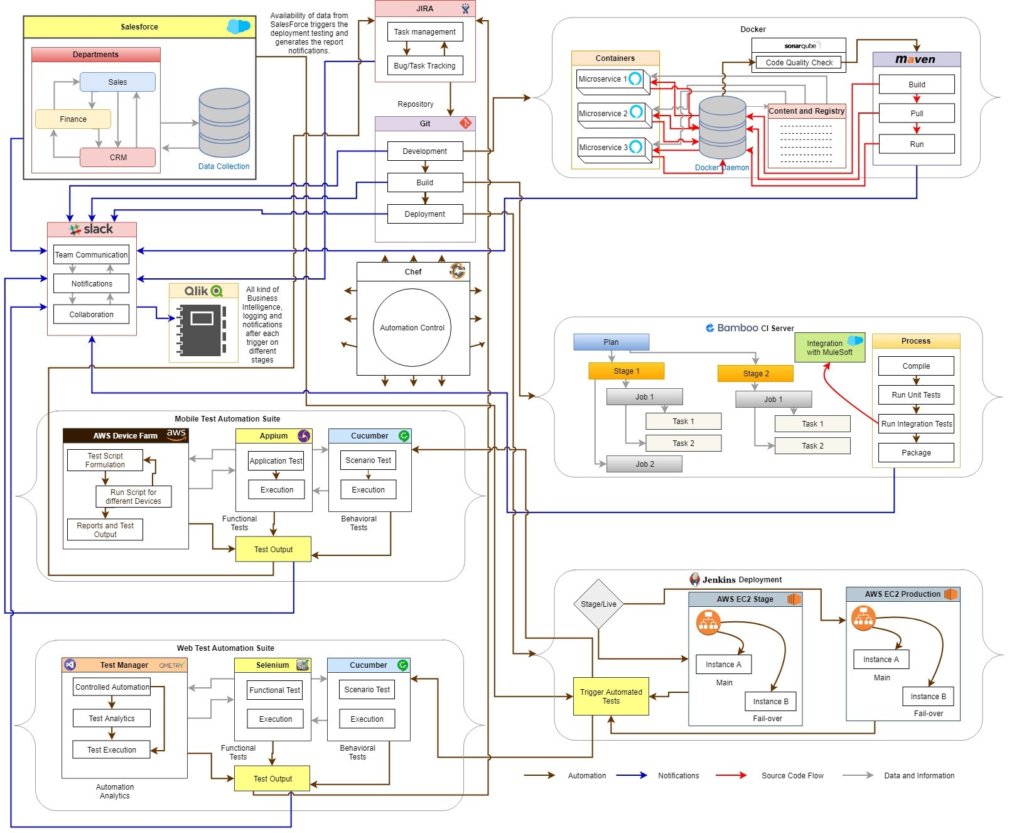
Below diagram will give an overview of what the context of this blog is:
AUTOMATION
Chef handles most of the automation in the life cycle through its scripts and all of the next steps are triggered as per the output of current step. At every step, teams are being informed via Slack and respective reports (using Qlik)are generated as well. To brief the process of automation, let’s understand the cycle as
Develop -> Build -> Deploy -> Test
Development is done through Docker based containers, where each container may contain 1 or more microservices. Docker Daemon handles the progress of microservices and accordingly triggers SonarQube to check the code quality of the developed microservice and once passed, goes via Maven Repository for build update and build-history maintenance.
The Integration happens through Bamboo Integration Server and unit tests are performed to get the builds checked. On a successful build, deployment is triggered over AWS EC2 instances.
Any of such Deployment triggers the automated tests which are complete suite managed separately for Mobile and web. Both the suites conduct the behavioral tests using Cucumber and Functional tests using Appium and Selenium for Mobile and Web respectively. AWS Device Farm is being used to make sure that mobile builds are verified over multiple devices and QMetry/MTM are used to perform the web automation to generate the complete test analytics for the overall output from Selenium and Cucumber.
CONCLUSION
The major emphasis of the solution was to implement the complete automation and development life cycle with increased performance and output efficiency. To conclude:
CI/CD and Automation life cycle reduces the development efforts upto 70%
Continuous Reporting and Bug tracking keeps the development on track and increases development efficiency.
Microservice helps in bug detection at very early stage of the development.