In this article, we’ll go over the Deployment Pipeline in Power BI and provide some useful information on Microsoft Power BI Consulting and development services.
and tagging of structured, unstructured, or semi-structured documents in document libraries.
SharePoint libraries have long been used as a file repository, but there was no way to organize, classify, sort, and group documents based on their content.
SharePoint Syntex solves the content extraction problem and implements classifications It not only aids in content extraction, but it can also generate the document based on the contents stored in the database.
For classification and extraction, SharePoint Syntex already includes two prebuilt models.
Power BI Deployment Pipelines - What are they?
A deployment pipeline is a tool used to handle the challenges of collaboration and efficiency. It enables BI scientists to design and control each stage of the workflow. These modules can be reprocessed to save time and improve productivity. It enables developers to generate and test content before making it available to real-world users in a production setting. These contents could include summaries, reports, the dataset itself, and a variety of other things.
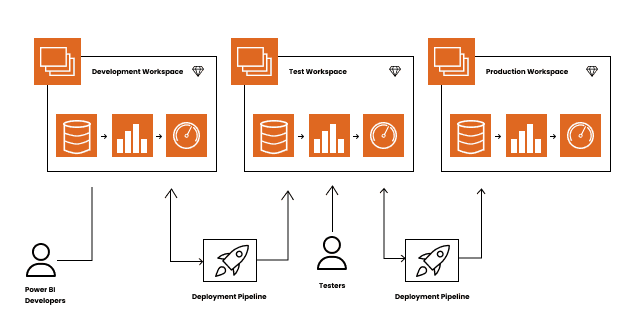
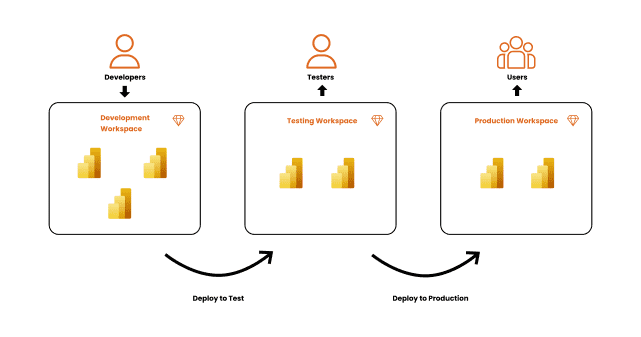
The Deployment Pipelines tool is a Power BI Service feature that allows developers to manage the development lifecycle of content within their domain. The tool is intended to be a reusable and efficient pipeline that automates content flow via three stages:
Development
In a development workspace, you can create, review, and update the material. Deploy the content to the test stage when it’s ready to be tested and reviewed
Attempt / Test
In this preproduction workspace, test and validate that the material is correct. Deploy the content to the production stage when it’s ready to be disseminated to your users.
Production
The workspace content has been thoroughly vetted and is available for your users to consume via an app or access to the production workspace.
- Create a deployment pipeline first
- Designate a work area
- Deploy to a new empty stage
- Create deployment rules in step four.
Why do we need a deployment pipeline?
The deployment pipeline allowed development teams to focus more on innovating and improving the end product for the user. By reducing the need for any manual tasks, teams can deploy new code updates much quicker and with less risk of any human error.
Using pipelines for deployment
Some considerations or prerequisites, which must be followed before getting started with Deployment pipelines.
1. Deployment pipelines are the Power BI premium feature so the user must have one of the following Premium licenses:
A) A Power BI Pro user that belongs to an organization that has Premium capacity –
Individual user licenses for Power BI Pro allow users to see and interact with reports and dashboards that have been published to the Power BI service by others. This licensing option allows users to collaborate and share content with other Power BI Pro users. Unless the content is hosted by a Power BI Premium capacity, only Power BI Pro users can publish or share content with other users, or consume content created by others.
Users without a Pro license can still access a workspace that’s in Power BI Premium capacity, as long as they’re assigned a role in that workspace. If the workspace owner creates an app based on content from that workspace, users without Pro licenses can view that app in Premium capacity.
B) Premium Per User (PPU)
Establishments can license Premium capabilities on a per-user foundation with Power BI Premium Per User. The Premium Per User (PPU) offers all the features of a Power BI Pro license, plus additional features such as paginated reports, AI, and other features obtainable only to quality/premium clienteles. PPU licenses include all the features of Power BI Pro licenses, so you do not need a distinct Pro license
2. Workspace Permissions
The Deployment Pipelines are created at the workspace level. The workspace must be a Premium workspace (created with a Premium account), and you must be the admin of that workspace. Workspaces are collaborative workspaces where you can develop collections of dashboards, reports, datasets, and paginated reports with your colleagues.
Note: Currently it is not possible to create deployment pipelines for workspaces created with a non-premium account. The premium workspaces will show up with a diamond
Make a pipeline for deployment
A pipeline can be created using the deployment pipelines tab or a workspace. After you’ve constructed the pipeline, you may either share it with other people or delete it. When you share a pipeline with others, the users with whom you share the pipeline gain access to it. Users with pipeline access can view, share, modify, and delete the pipeline. Make a pipeline by giving it a name and a description in the Create a deployment pipeline dialog box.
Select Deployment pipelines from the navigation pane in the Power BI service, then create a pipeline. In the Create a deployment pipeline dialog box, enter a name and description for the pipeline and select Create. You can also create a pipeline from an existing workspace, providing you’re the admin of a new workspace experience.
Here is a Microsoft blog about creating the deployment pipelines
Use deployment rules with a real-life data source
- If you’re using the test stage to simulate real-life data usage, it’s recommended to separate the development and test data sources. The development database should be relatively small, and the test database should be as similar as possible to the production database. Use data source rules to switch data sources in the test stage
- Controlling the amount of data, you import from your data source is useful if you’re using a production data source in the test stage. To do this, add a parameter to your data source query in Power BI Desktop. Use parameter rules to control the amount of imported data or edit the parameter’s value. You can also use this approach if you don’t want to overload your capacity.
Dataset limitations
- Datasets that use real-time data connectivity can’t be deployed.
- A dataset with Direct Query or Composite connectivity mode, that uses variation or calendar tables, isn’t supported. · During deployment, if the target dataset is using a live connection, the source dataset must use this connection mode too.
- After deployment, downloading a dataset (from the stage it’s been deployed to) isn’t supported.
Data sources – The Deployment Pipelines feature supports the following data sources:
- Azure Analysis Services
- Azure Synapse
- SSAS
- Azure SQL Server
- SQL Server
- OData feed
- Oracle
- SAP Hana (only the import mode)
- SharePoint
- Teradata
Microsoft Power BI Consulting Services with Ignatiuz
A wide range of businesses rely on our Power BI consultants for business intelligence and data visualization. Our Power BI Consulting Service includes a complete consultation to identify gaps and opportunities by employing Power BI to provide strong insights via dashboards and data visualization. Power BI is a Microsoft application that uses business intelligence to give enterprises a 360-degree perspective of their operations
We aim to give you those insights so you can make informed decisions based on all aspects of the company. Contact us today to learn more about Power BI deployment pipelines—or enhanced analytics.
